| Pulling And Lifting Machine |
|
|
|
|
| Multipurpose, Portable, Universal, Gearless, Hand operated Pulling and Lifting machine, Supplied complete with telescopic, operating handle and standard Length of super flex steel fibre-mixed core wire-rope fitted with Hook or Shackle at one end and fused and tapered at the other end. |
|
| Pulling & Lifting Machines Hy-Tack XL Series 2005 |
|
|
Technical Specifications
|
HT-7
|
HT-13
|
HT-20
|
HT-35
|
HT-58
|
|
Dimensions (Approx.)
|
515 x 265 x 110
|
600 x 360 x 155
|
620 x 360 x 155
|
720 x 400 x 160
|
810 x 465 x 190
|
|
Capacity (SWL) (kgs) Lifting, Pulling
|
750, 1250
|
1600, 2600
|
2000, 3000
|
3200, 5200
|
5000, 8000
|
|
Length of Telescopic operating handle (Approx.)
|
54/72 cm
|
66/104 cm
|
70/130 cm
|
79/118 cm
|
120/145 cm
|
|
Effort at full load (Approx.) kgs
|
40
|
50
|
50
|
60
|
70
|
|
Rope travel per Return stroke (Approx.) mm
|
40
|
55
|
50
|
36
|
30
|
|
Diameter of wire Rope (mm)
|
8.0
|
11.3
|
12.0
|
16.3
|
20.0
|
|
Standard Length with Each machine (meters)
|
10
|
20
|
20
|
10
|
10
|
|
breaking Load of wire rope (Approx.)
|
4.5 Tons
|
9.0 Tons
|
10.0 Tons
|
18.0 Tons
|
24.0 Tons
|
|
|
| Exclusive Features |
|
Casing:
|
Made from CRC sheet (Galvanized) or Graded Aluminium for
light weight a high factor of safety. |
|
Jaw:
|
Made from Special Alloy Steel, Accurately Machined, so as
to avoid slippage of wire rope. |
|
Jaw Limits:
|
Are made from special steel & heat treated for greater strength. |
|
Hooks / D-shackles:
|
Fitted with Alloy steel Forged Hooks or D-shackle to make
it feasible to be able to fit it at any place. |
|
Wore Ropes:
|
Super flex Steel Fiber -mixed are, manufactured as IS. 226. |
|
|
| Accepted & Widely used by |
- Railways
- Mines and Quarries
- Navigator
- Electricity Board???s
- Dockyards
- Road Transports
- Heavy Industries etc.
|
|
|
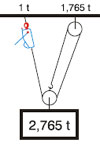
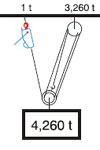
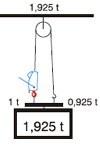
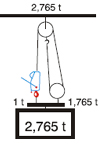
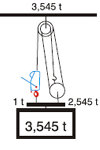
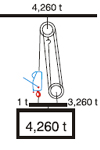
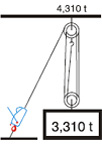
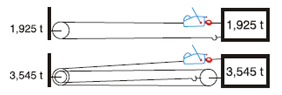
| Increase of Pulling and Lifting Power: |
|
| Lifting - machine anchored above load |
|
|
|
| Lifting - machine anchored to load |
|
|
|
| Lifting - machine anchored at ground level |
|
|
|
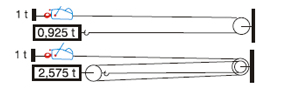
| Pulling - Case No. 1 |
|
|
|
| Pulling - Case No. 2 |
|
|
|
| Pulling - machine attached to load |
|
|
|
| For General Work on Site: |
|
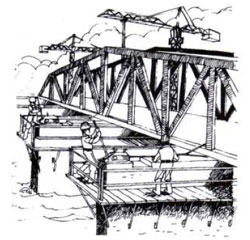
| Many applications for bridge building such as: |
|
Moving of support for concrete forms
Support of under-slung formwork
Pulling per-cost concrete beams, etc,
|
|
|
|
|
Fig 4.1
|
Fig 4.2
|
|
|
|
|
Fig 4.3
|
Fig 4.4
|
|
|
| Railway uses ( buildings and permanent way): |
- Siting and joining of rails (fig.4.2)
- Assembling, dismantling or maintenance of points and crossing with smaller teams and without the risk of distortion of the track
- Replacement of electric cable in gutters or under the track
- Lifting sections of track for replacing ballast and sleepers
- Cable tnsioning for points and signals
- Lifting (or removal) of pylons and signals (fig. 4.1)
- Maintenance and tensioning of catenaries, etc.
|
| Operations: |
- Emergency operation of frozen points
- Re-railing work
- Replacing friction buffer stops
- Giding & lifting rails
- Loading trucks on lorries in case of changing track (railway tracks of different gauge)
- Shunting or unloading wagons in small stations, etc.
- Removing crash wreckage
- Equipment of plate-layer special trucks (welded rails 215m. long.)
- Replacing ballasts with gantry cranes
- Checking compression and rod-system of steam engine
- Equipment for rescue carriage and trains
|
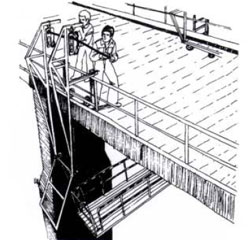
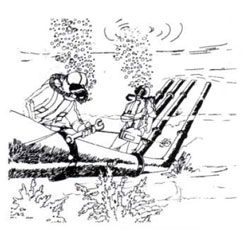
| Pipe laying and joining. |
- Special rigs have been constructed using Pulling Lifting Machines for the jobs of both laying large diameter concrete pipes and for pulling them together for jointing (fig. 2.1 & 2.2)
- Cleaning out pipes and sewers
- Pulling a carriage through steel pipelines for welding, x-ray inspection of welding joints concrete coating, etc.
- Positioning of pipes for welding (fig.2.3)
- Under water pipeslines assembly (fig.2.4)
- pulling pipes through tunnels (fig.2.5)
|
 |
|
fig. 2.1
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fig. 2.2
|
Fig 2.3
|
|
|
|
|
Fig 2.4
|
Fig 2.5
|
|
|
| For Shipbuilding and Marine Engineering |
- Handling large plates
- Erecting masts and booms
- Suspending welders', riveters' and painters' cradles (fig3.3)
- Centralizing ship in dry dock (fig.3.1)
- Lifting engine covers
- Installing engines (fig.3.4)
- Pulling through tail shafts
- Installing and removing propellers
- Emergency operation of davits
- Opening hatches
- Handling hold covers (Mc Gregor system)
- Lifting small boats out of the water (fig 3.5)
- Dragging boats ashore
- Pulling together pushers and barges of floating merchandise trains (fig.3.2)
|
 |
|
fig. 3.1
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fig. 3.2
|
Fig 3.3
|
|
|
|
|
Fig 3.4
|
Fig 3.5
|
|
|
| Trucks |
 |
|
Fig 1.1
|
 |
|
Fig 1.2
|
|
- Debogging of trucks (fig1.1)
- Tensioning heavy and bulk loads on trucks (fig.1.2)
- Loading onto trucks (fig.1.3)
|
| Rigging and maintenance of construction euipment |
- Changing and tensioning tracks and conveyor belts
- Changing and tensioning excavator ropes (fig1.4)
- Handling excavator jibs
- Erecting tower cranes (fig 1.5)
|
| Miscellaneous |
- Removal of a site cabin (fig 1.6)
- Tensioning of safety-nets on construction sites (fig1.7)
|
| Fixing heavy girders |
- When a girder is lowered in position by a crane, it may not be in a suitable position for bolt hole line-up, A Pulling Lifting Machine can be used to pull it until holes line-up.
|
| Erecting steel silos |
- Assemble at ground level, then lift section after section (fig.1.8 & 1.9)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fig. 1.3
|
Fig 1.4
|
|
|
|
|
Fig 1.5
|
Fig 1.6
|
|
|
 |
|
Fig 1.7
|
Fig 1.8
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fig 1.9
|
|
|